Don't miss our Corporate Gifting Offer - up to 20% OFF!
Millets Forever
Why Millets?
“Often overlooked, millets are tiny powerhouses of nutrition, making a big comeback! These ancient grains, cultivated for thousands of years, are not just a food source; they are a key to unlocking better health and a more sustainable future.
Why are Millets So Important?
For Your Health:
- Nutrient-Dense: Packed with essential vitamins (B complex), minerals (iron, calcium, magnesium, zinc), and antioxidants.
- High in Fiber: Aids digestion, promotes gut health, and helps manage weight.
- Gluten-Free: A natural alternative for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
- Low Glycemic Index (GI): Helps regulate blood sugar levels, making them excellent for managing diabetes.
- Rich in Protein: Contributes to muscle repair and overall body function.
- Heart Healthy: Can help reduce bad cholesterol and blood pressure, promoting cardiovascular well-being.
For Our Planet:
- Drought-Resistant: Thrives in arid conditions with minimal water, making them ideal for water-scarce regions.
- Low Carbon Footprint: Requires fewer inputs (fertilizers, pesticides) and releases fewer greenhouse gases compared to other major crops.
- Soil Enhancers: Improve soil fertility and biodiversity, contributing to healthier ecosystems.
- Climate-Resilient: A crucial crop for food security in a changing climate.
By choosing millets, you’re not just making a healthy choice for yourself; you’re supporting a healthier planet and resilient farming communities. It’s truly food that does good!”
India: The Cradle of Millets – A Heritage Revived
“India holds a significant place in the global history of millets. For centuries, these resilient grains were a staple food across diverse regions of the subcontinent, forming the backbone of traditional Indian agriculture and diets. From the arid plains of Rajasthan to the fertile Deccan plateau, Indian farmers have cultivated a rich variety of millets, deeply embedded in local cuisines and cultural practices.
A Rich Legacy, A Promising Future:
While the Green Revolution shifted focus to other crops, millets are now experiencing a powerful resurgence, driven by growing awareness of their health benefits and environmental resilience. India remains one of the largest producers of millets globally, contributing significantly to the world’s millet supply.
At Paripoorn Foods, we are proud to be part of this revival. We work closely with Indian farmers, supporting their efforts to cultivate these indigenous grains. Our commitment to Indian millets production means:
- Supporting Local Economies: Investing directly in the agricultural communities across India.
- Preserving Biodiversity: Encouraging the cultivation of diverse native millet varieties.
- Promoting Sustainable Farming: Advocating for traditional and eco-friendly farming methods that have sustained our land for generations.
By sourcing our millets from Indian farms, we not only ensure the highest quality and freshest ingredients for your snacks but also contribute to the economic prosperity and ecological well-being of our homeland.”
- Millets are highly adaptive to a wide range of ecological conditions and thrive well in rain-fed; arid climate and they have minimal requirement of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Health-promoting nutritious crop: Compared to other cereals they have superior micronutrient profile and bioactive flavonoids.
- Millets have a low Glycaemic Index (GI) and also associated with the prevention of diabetes.
- They are good source of minerals like iron, zinc, and calcium.
- Millets are gluten-free and can be consumed by celiac disease patients.
- Millet has a beneficial effect on the management and prevention of hyperlipidemia and risk of CVD.
- In India, Millet is generally consumed with legumes, which creates mutual supplementation of protein, increases the amino acid content, and enhances the overall digestibility of protein.
- Millet based value-added products in ready to cook, ready to eat category are easily accessible and convenient to the urban population.
- Millets are used for dual purposes as food as well as fodder, which make it more farming efficient.
Meet the Millet Family: Diverse Grains, Diverse Benefits
“India holds a significant place in the global history of millets. For centuries, these resilient grains were a staple food across diverse regions of the subcontinent, forming the backbone of traditional Indian agriculture and diets. From the arid plains of Rajasthan to the fertile Deccan plateau, Indian farmers have cultivated a rich variety of millets, deeply embedded in local cuisines and cultural practices.
A Rich Legacy, A Promising Future:
While the Green Revolution shifted focus to other crops, millets are now experiencing a powerful resurgence, driven by growing awareness of their health benefits and environmental resilience. India remains one of the largest producers of millets globally, contributing significantly to the world’s millet supply.
At Paripoorn Foods, we are proud to be part of this revival. We work closely with Indian farmers, supporting their efforts to cultivate these indigenous grains. Our commitment to Indian millets production means:
- Supporting Local Economies: Investing directly in the agricultural communities across India.
- Preserving Biodiversity: Encouraging the cultivation of diverse native millet varieties.
- Promoting Sustainable Farming: Advocating for traditional and eco-friendly farming methods that have sustained our land for generations.
By sourcing our millets from Indian farms, we not only ensure the highest quality and freshest ingredients for your snacks but also contribute to the economic prosperity and ecological well-being of our homeland.”
Millet is a type of grain that is popular in many parts of the world, especially in Africa and Asia. It is a staple food in many parts of the world, particularly in Africa and Asia. According to the World Food Programme, there are an estimated 1.2 billion people who consume millet as a part of their diet.
Millet production has remained relatively stable over the past few years, with an estimated production of 28 million metric tons in 2020. The majority of millet is produced in Africa, followed by Asia. India is the largest producer of millet, followed by Niger and China. Other major millet-producing countries include Burkina Faso, Mali, and Senegal.While millet is not a major food crop in the developed world, it plays a vital role in the diets of many people in developing countries. Millet is a drought-tolerant crop that can be grown in dry, arid climates where other crops would fail. It is also a nutritious grain that is high in fiber and essential minerals. For these reasons, millet will continue to be an important food crop in the years to come.
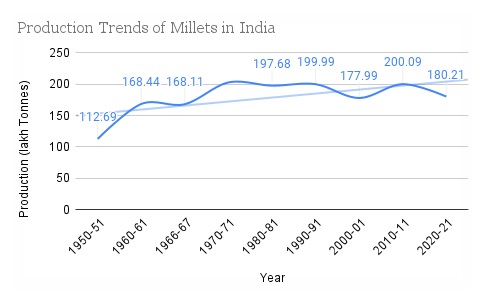
In India, millet production has been on the rise in recent years. India is one of the largest producers of millets &Indian farmers have been increasingly planting millet as a drought-resistant crop. The Indian government has also been promoting millet production as part of its National Food Security Mission. As a result of these factors, millet production in India is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The graph below depicts the production trends of millets in India.
Common name of Millets in Indian Languages

Marathi : Jwari
Oriya : Juara
Punjabi : Jowar
Tamil : Cholam
Telugu : Jonna

English: Sorghum
Bengali : Jowar
Gujarati : Jowari, Juar
Hindi : Jowari, Juar
Kannada : Jola

English :Pearl Millet
Bengali : Bajra
Gujarati : Bajri
Hindi : Bajra
Kannada : Sajje

Marathi : Bajri
Oriya : Bajra
Punjabi : Bajra
Tamil : Kambu
Telugu : Sajja

English : Finger Millet
Bengali : Marwa
Gujarati : Nagli, Bavto
Hindi : Ragi, Mandika,
Marwah
Kannada : Ragi

Marathi : Nagli, Nachni
Oriya : Mandia
Punjabi : Mandhuka, Mandhal
Tamil : Keppai, Ragi, Kelvaragu
Telugu : Ragi Chodi

English : Foxtail Millet
Bengali : Kaon
Gujarati : Kang
Hindi : Kakum
Kannada : Navane

Marathi : Kang, Rala
Oriya : Kanghu, Kangam,
Kora
Punjabi : Kangni
Tamil : Tenai
Telugu : Korra

English : Barnyard Millet
Bengali : Shyama
Gujarati : ….
Hindi : Sanwa
Kannada : Oodalu

Marathi : …
Oriya : Khira
Punjabi : Swank
Tamil : Kuthiraivolly
Telugu : Udalu, Kodisama

English : Kodo Millet
Bengali : Kodo
Gujarati : Kodra
Hindi : Kodon
Kannada : Harka

Marathi : Kodra
Oriya : Kodua
Punjabi : Kodra
Tamil : Varagu
Telugu : Arikelu, Arika

English : Little Millet
Bengali : Sama
Gujarati : Gajro; Kuri
Hindi : Kutki, Shavan
Kannada : Same, Save

Marathi : Sava, Halvi, vari
Oriya : Suan
Punjabi : Swank
Tamil : Samai
Telugu : Samalu

English : Proso Millet
Bengali : Cheena
Gujarati : Cheno
Hindi : Chena; Barri
Kannada : Baragu

Marathi : Vari
Oriya : China Bachari bagmu
Punjabi : Cheena
Tamil : Pani varagu
Telugu : Variga
Benefits of Eating Millets

Nutrient-Rich:
Millets are rich in essential nutrients like protein, fiber, vitamins (especially B-vitamins), and minerals (such as magnesium, iron, and phosphorus).They provide antioxidants which help in combating oxidative stress and inflammation.

Low Glycemic Index:
Millets have a low glycemic index, which helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. This makes them a good option for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar.

High Fiber Content:
The high fiber content in millets aids in digestion, helps prevent constipation, and promotes a feeling of fullness, which can assist in weight management.

Health-Conscious Consumers
The primary target market would include individuals who prioritize health, wellness, and sustainability in their dietary choices.

Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly:
Millets are resilient crops that require less water and can grow in less fertile soil. This makes them a sustainable option for agriculture, contributing to food security and environmental conservation.

Versatility:
Millets can be used in a variety of snack forms, including chips, bars, puffs, and more, offering diverse options for consumers.
